
Sony Alpha camera supported by Sony SDK (Software Development Kit)

Sony Alpha camera supported by Sony SDK (Software Development Kit)

Digital Video Camera using various interfaces (USB, Gigabit Ethernet, Camera link)
This LiDAR depth sensor adopts the “Direct Time of Flight (dToF) method*1,” which delivers highly accurate measurement, distance resolution*2, and measuring range.
By employing the proprietary dToF ranging module equipped with a Single Photon Avalanche Diode (SPAD)*3 sensor, and by utilizing multiple ranging points for distance measurement, it can accurately measure distances in three dimensions: length, width, and depth. Furthermore, it can also measure distances to low-contrast objects, objects with low reflectivity, which are more difficult to detect using other ranging methods.
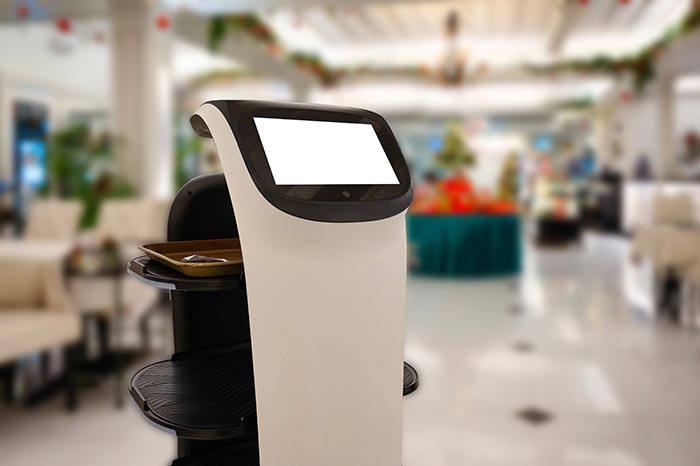
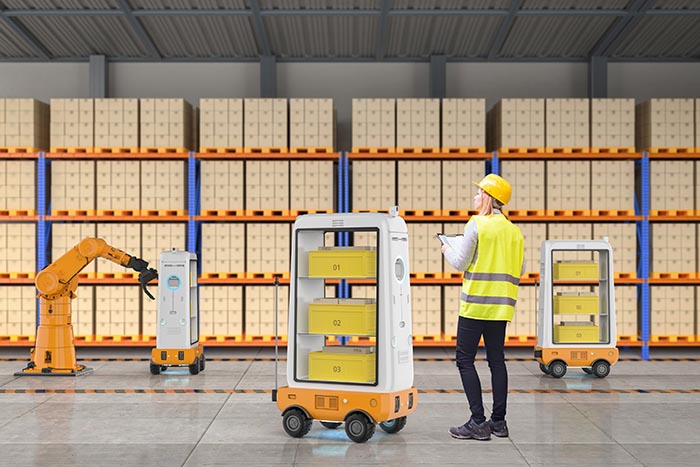
This enables accurate distance measurement in environments such as retail stores, where various objects, including people and fixtures, are expected. In addition to its ability to accurately measure the distance to objects both indoors and outdoors, the sensor's compact, lightweight design and robust aluminum housing allows it to be integrated into various devices, such as food serving robots in restaurants, autonomous mobile robots in warehouses, and drones used for inspections and surveys.
By employing Sony’s proprietary dToF ranging module equipped with a SPAD sensor, it enables highly accurate ranging measurement and distance resolution. It can measure at various distances, for example, at 10 meters with a margin of ±5 cm both indoors and outdoors. Furthermore, it can accurately measure the distance to various objects, which is difficult with other ranging measurement methods. This includes the low-contrast objects, objects with low reflectivity, and objects floating in the air, making it suitable for integration into robots used in environments such as warehouses and stores where various objects are mixed together.
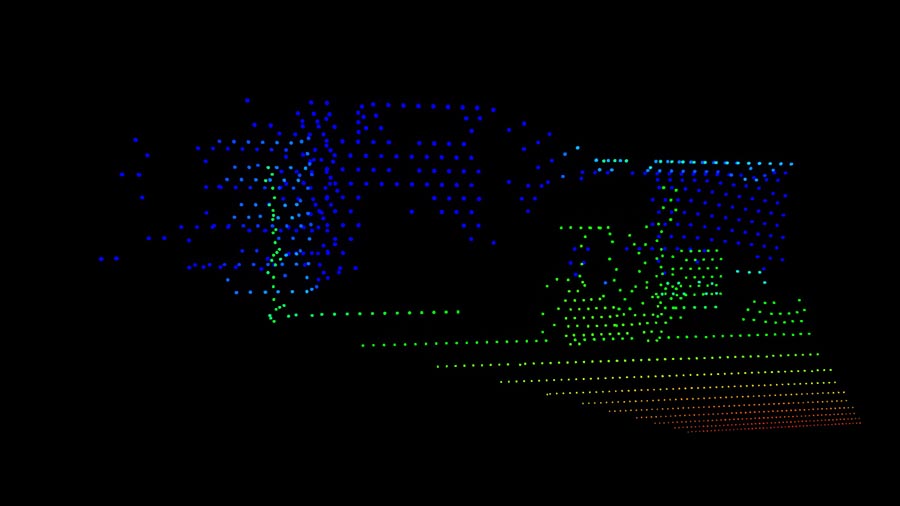
An example of ranging measurement data displayed as point cloud data (an image for illustration purposes only)

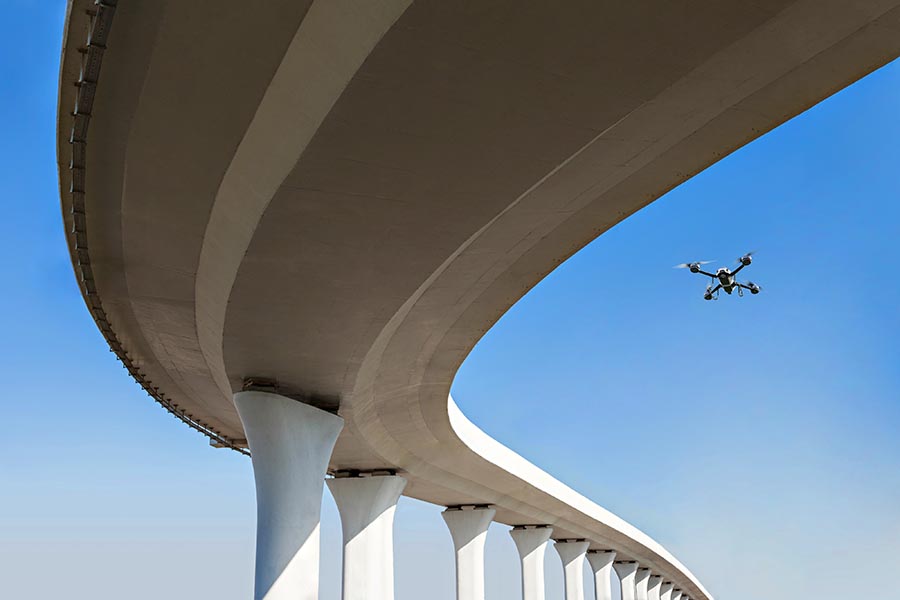
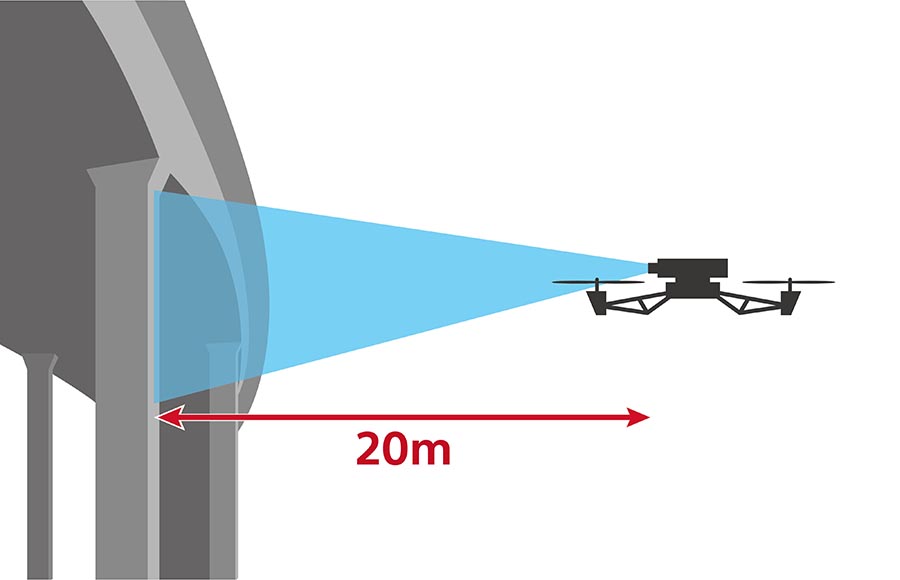
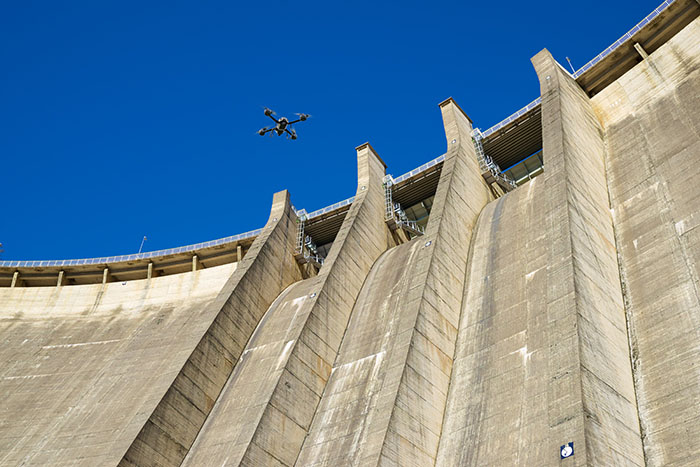
Its ranging measurement is highly accurate; even from a long distances of 40 meters indoors and 20 meters*4 outdoors on a clear summer day (assuming 100,000 lux). This measurement accuracy, from a distance even outdoors, makes it very useful to measure distances to objects that are difficult for people to approach, such as bridges, expressways, and dams.

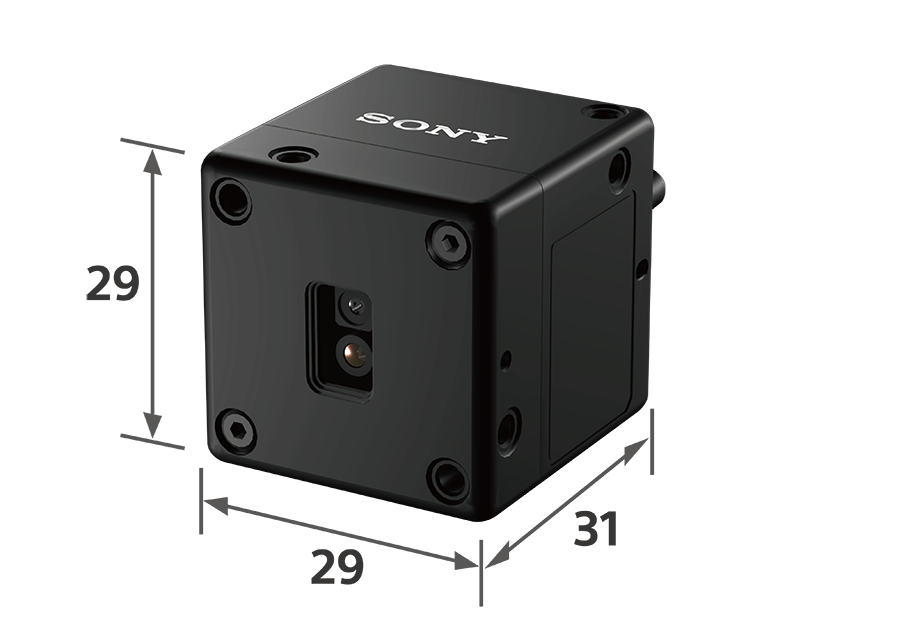
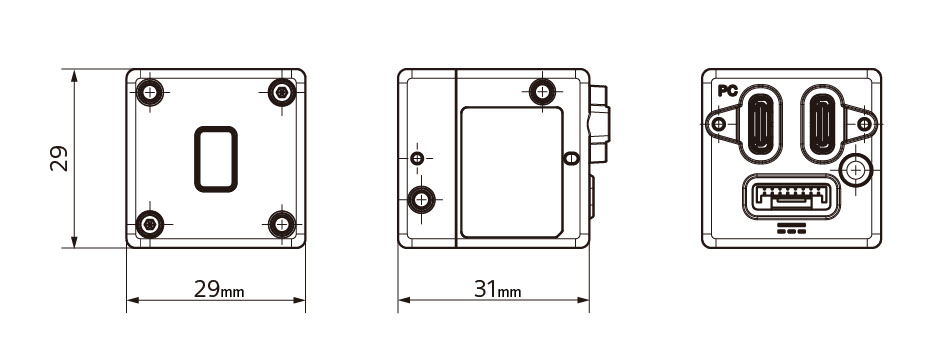
Housing This is the world's smallest and lightest*5 sensor; 29 mm in width x 29 mm in height x 31 mm in depth*6, with 50 g in weight. The use of an aluminum alloy for the housing achieves both lightness and robustness. This compact housing makes it easy to integrate into various devices, such as autonomous mobile robots with limited space for depth sensors, and drones where weight affects the flight distance.


This device is capable of accurately measuring distances in environments such as stores, where various objects, including people and fixtures, are expected. The range of applications will be expanded by integrating it into various devices, such as food serving robots in restaurants, autonomous mobile robots in warehouses, and drones used for inspections and surveys.



| Features | Specification |
| HFoV | 30° or more *4 |
| Maximum measurement range @15 fps, 50% reflectivity, center |
Indoor: 40 meters*4 Outdoor: 20 meters*4 |
| Measurement accuracy @10m |
Indoor/Outdoor: ±5 cm *4 |
| Distance resolution | 0.25 mm |
| Frame rate | 30 fps 15 fps @ Maximum ranging distance mode |
| Number of ranging points | 576 (24x24) |
| Laser wavelength | 940 nm |
| Dimensions | W29 x H29 x D31 mm (excluding protrusions) *4 |
| Weight | 50g or less*4 |